Government contractors have a critical role in helping the Department of Defense (DoD) secure the Defense Industrial Base. These contractors will need to be assessed for the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) by a Certified Professional (CP) with a CMMC Third-Party Assessor Organization (C3PAO). Becoming an auditor is a multi-step process.
What is CMMC certification?
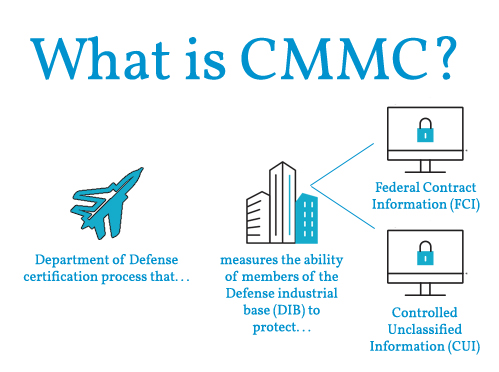
The DoD introduced the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification process to enhance the cybersecurity posture of the Defense Industrial Base and its supply chain. This verification process ensures that appropriate cybersecurity practices and processes are in place across the thousands of DoD industry partners and suppliers.
CMMC is a robust, third-party certified cybersecurity model that all but guarantees tighter cybersecurity among government contractors. CMMC defines the activities, procedures, compliance requirements and certifications expectations, using a framework based on the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-171.
The CMMC framework outlines the cybersecurity practices prime contractors and all of their subcontractors need to follow to protect controlled unclassified information (CUI) within the government supply chain.
CMMC defines five cybersecurity maturity levels, ranging from basic cyber hygiene (ML-1) to advanced cybersecurity practices (ML-5). Each level outlines the cybersecurity requirements, capabilities, processes, and practices that reduce the risk of a security breach.
CMMC certification requirements
Achieving a certification level requires validation by a CMMC Third-Party Assessment Organizations (C3PAO) that has been authorized and trained by the CMMC Accreditation Body (AB), a nonprofit organization. The DoD will confirm a company’s Maturity Level Certification when making the award on a contract.
CMMC represents a giant step forward for the contractor industry. Previously, cybersecurity compliance was self-assessed under DFARS 252.204-7012, leaving room for lax adherence to the policies. By requiring a third-party assessment, the CMMC applies rigor and standard benchmarks for cybersecurity practices, giving the DoD higher confidence that organizations are meeting the requirements.
Every company within the DoD supply chain, approximately 300,000 prime contractors and subcontractors, will need to be certified at a CMMC maturity level to contract with the DoD. Recertification will be required at least every three years. Practices, however, will be updated continuously to reflect evolving threats and security needs.
All those companies within the Defense Industrial Base need to familiarize themselves with the security requirements outlined in CMMC and consider their needed Maturity Level, which is often a reflection of the CUI or other DoD data stored or processed on their networks. Without the required level of certification for a particular solicitation, a company will not be able to accept the contract award.
Those companies without cybersecurity expertise on staff may need outside subject matter experts (SME) to determine how they stack up to required practices. Those companies with internal resources or who have outsourced IT help, may also want to consider a third-party readiness review to verify that their practices are meeting the required CMMC standards.

The CMMC audit process, training and how to successfully become a CMMC auditor
The CMMC audit process is rigorous, reflecting the serious nature of cybersecurity requirements.
When a company is prepared, they register with the accreditation authority, the CMMC-AB. The company will then select a C3PAO from the CMMC-AB marketplace and provide the results of any readiness assessments or self-reviews and the Maturity Level sought.
The C3PAO Auditor, also called an Assessor, will review the information to determine if the company is ready for a review and confirm that they understand the scope. They will also negotiate terms and costs. The CMMC Auditor will also determine a timetable for the assessment with the company agreeing to provide necessary personnel and access.
The C3PAO’s cost and timing are based on staffing ability, the network architecture being assessed, and the number of network assets and physical locations that need to be assessed.
If the Auditor determines the company is not ready for the assessment, they will inform them why they are not ready, however they cannot offer any suggestions on how to close those gaps.
The path to becoming a CMMC auditor isn’t complex for those already familiar with cybersecurity protocols and best practices but will require both coursework and an exam. Because CMMC itself is still being finalized, course materials and exams are not finalized.
The CMMC-AB has run at least 100 provisional instructors through their program. The provisional instructors are authorized to teach Certified CMMC Professional (CCP) and Certified CMMC Assessor (CCA) coursework.
To start the process now, submit an application for a Certified Assessor and the $200 fee on the CMMC-AB website and begin taking provisional CCP coursework and doing self-study.
Auditor training courses should cover basic topics:
- Defining CUI and FCI (and regulations)
- Contributing cybersecurity frameworks
- How to read the CMMC model documentation
- How to perform CMMC Level 1 scoping
- The “CMMC Assessment Process”
- CMMC Level 1 practices
Assuming you’ve already been working on CMMC projects, the primary benefit you get from the coursework will be to learn as an assessor what is acceptable or not acceptable.
Your class should have discussions about various practices to identify the minimum expectations for each practice. Ideally, the class should also discuss commonly misunderstood practices, especially ones where assessors could introduce their own biases.

CMMC training provider: choose wisely
The CMMC-AB and DoD have not yet provided final course outlines. Several companies are building content for what they think will be required, but they won’t know for sure until the final CMMC curriculum is released.
The CMMC-AB Marketplace lists Licensed Partner Publishers in good standing but does not verify whether their materials have been approved for use in courses. This is relevant because the CMMC-AB has stated that the mandatory training for Certified CMMC Professional (CCP) and Certified CMMC Assessor (CCA) is only recognized if the course materials are approved.
For individuals looking to become provisional auditors or assessors, and companies preparing for CMMC certification, DTS is a one-stop resource for expert advice and implementation answers. Our consultants are on the leading edge of CMMC best practices. Visit DTS: Contact page to schedule a call with one of our cybersecurity professionals.


